The Sumerians, who inhabited the region of modern-day southern Iraq, emerged around 4500 BCE. They were pioneers in various fields, including agriculture, writing, mathematics, and governance. Their cities, such as Uruk and Ur, thrived with impressive infrastructure, intricate temples, and bustling trade networks.
For over three millennia, the Sumerians flourished, leaving behind a lasting impact on subsequent civilizations. However, like all great empires, their decline was inevitable. The exact reasons for their fall are not entirely clear, but several factors played a role in their demise.
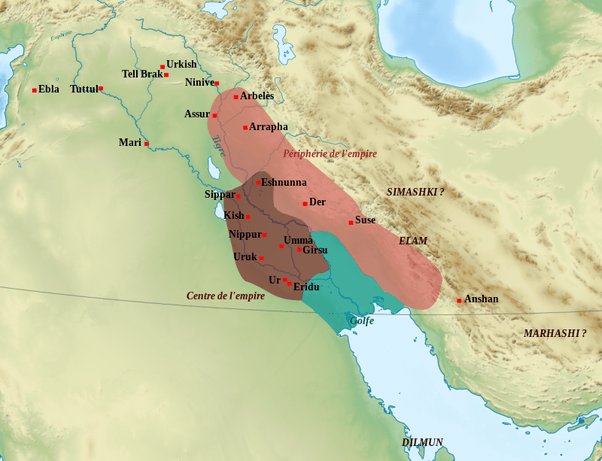
One significant factor was invasions from neighboring peoples. Around 2000 BCE, the Akkadians, led by Sargon of Akkad, conquered the Sumerian city-states and established the Akkadian Empire. This marked the beginning of foreign rule in Mesopotamia.
Despite this, Sumerian culture continued to influence the region, and the city of Ur experienced a revival during the Third Dynasty of Ur (2112–2004 BCE). During this period, the Sumerians enjoyed a brief renaissance, constructing grand buildings, improving irrigation systems, and engaging in prosperous trade.
However, the empire faced internal conflicts and external threats from the Elamites and Amorites. These factors, combined with natural disasters like droughts and floods, weakened the Sumerian civilization.
Around 1900 BCE, the Elamites sacked Ur, effectively bringing an end to the Third Dynasty of Ur. This event marked the final blow to Sumerian dominance in Mesopotamia. Subsequently, the region fell under the control of the Babylonians, who built their own empire upon the remnants of Sumerian culture.
Despite its decline, the Sumerian civilization had a lasting legacy. Their invention of writing, the cuneiform script, influenced numerous cultures in the ancient Near East. Additionally, their legal codes, such as the famous Code of Ur-Nammu and the Code of Hammurabi, laid the groundwork for future legal systems.
In terms of duration, the Sumerian civilization lasted for approximately three millennia, starting around 4500 BCE and ending around 1900 BCE. It is remarkable to consider that this civilization thrived for such a lengthy period, considering the challenges they faced throughout their history.
https://www.quora.com/How-did-Ancient-Sumerian-civilization-end-and-how-long-did-it-last

Interesting history! Gerry, do you write answers (and/or ask questions) on Quora? I used to (pre-Quora). Even was a “top Quora writer” in 2018, LOL! Thinking of starting again…
LikeLike